Inventory management is a critical aspect of supply chain management that involves overseeing and controlling the flow of goods and materials within a business. Effective inventory management ensures that the right products are available at the right time, in the right quantity, and at the right location. This article will explore the process, techniques, and benefits of inventory management in detail.
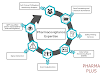
The Inventory Management Process
The inventory management process typically involves the following key steps:
Demand Forecasting: Accurate demand forecasting is the foundation of effective inventory management. By analyzing historical sales data, market trends, and customer preferences, businesses can estimate future demand and plan their inventory levels accordingly.
Inventory Planning: Based on demand forecasts, businesses determine optimal inventory levels for different products. This involves setting minimum and maximum stock thresholds, reorder points, and safety stock levels to ensure adequate availability while minimizing excess inventory.
Procurement and Replenishment: Once inventory levels reach the reorder point, businesses initiate procurement activities to replenish stock. This involves identifying reliable suppliers, placing purchase orders, and managing lead times to ensure timely delivery.
Receiving and Inspection: Upon receiving the ordered inventory, businesses conduct quality inspections and verify the received quantities against purchase orders. This step helps identify any discrepancies or damages and ensures that only high-quality products are accepted into the inventory.
Inventory Tracking and Control: Businesses employ inventory tracking systems to monitor stock levels, movements, and locations. This enables real-time visibility into inventory status, allowing businesses to identify slow-moving or obsolete items, prevent stockouts, and optimize inventory turnover.
Stock Storage and Organization: Proper storage and organization of inventory are crucial for efficient inventory management. Categorizing products, implementing a logical storage layout, and using inventory management software can help streamline picking, packing, and order fulfillment processes.
Order Fulfillment: When customer orders are received, businesses pick, pack, and ship the products from the available inventory. Accurate order fulfillment ensures customer satisfaction and helps maintain a positive reputation.
Inventory Analysis and Optimization: Regular analysis of inventory data helps identify trends, patterns, and opportunities for improvement. By applying inventory optimization techniques, such as ABC analysis, Economic Order Quantity (EOQ), and Just-in-Time (JIT) principles, businesses can optimize inventory levels, reduce carrying costs, and improve overall operational efficiency.
Techniques of Inventory Management
Inventory management is a critical aspect of supply chain management that involves controlling and overseeing the flow of goods and materials within a business. Different types of inventory management techniques and strategies are employed based on the specific needs and characteristics of the business. In this article, we will explore some commonly used types of inventory management approaches.
1. Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory Management
Just-in-Time (JIT) inventory management is a strategy aimed at minimizing inventory levels by receiving goods from suppliers only when they are needed for production or customer orders. This approach helps businesses reduce carrying costs associated with excess inventory, minimize waste, and improve operational efficiency. JIT inventory management relies on efficient coordination with suppliers, accurate demand forecasting, and reliable transportation and logistics systems to ensure timely delivery of materials.
2. Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) is a mathematical model used to determine the optimal order quantity that minimizes total inventory costs. It takes into account factors such as ordering costs (e.g., purchase costs, setup costs) and carrying costs (e.g., storage costs, holding costs). The EOQ model helps businesses strike a balance between ordering costs and carrying costs to achieve cost-effective inventory management. By calculating the EOQ, businesses can determine the ideal order quantity that minimizes overall costs.
3. ABC Analysis
ABC analysis is a technique used to categorize inventory items based on their value and importance. It helps businesses prioritize their inventory management efforts and allocate resources effectively. The analysis classifies inventory items into three categories:
- A-items: These are high-value items that contribute to a significant portion of revenue. They require careful monitoring, accurate forecasting, and efficient inventory control.
- B-items: These are moderate-value items that have a moderate impact on revenue. They are managed with less scrutiny compared to A-items.
- C-items: These are low-value items that have minimal impact on revenue. They are managed with less emphasis and may have higher stock levels.
By categorizing inventory items based on their value and focusing on A-items that generate the most revenue, businesses can optimize their inventory management efforts and ensure that critical items are always available.
4. Consignment Inventory
Consignment inventory is an arrangement between a supplier and a customer where the supplier retains ownership of the inventory until it is consumed or sold by the customer. In consignment inventory management, the supplier maintains the inventory at the customer's location, and the customer pays for the goods only when they are used or sold. This approach helps businesses reduce their inventory carrying costs while ensuring that the necessary items are readily available.
5. Dropshipping
Dropshipping is a fulfillment method where businesses do not keep inventory in stock. Instead, when a customer places an order, the business purchases the product from a third-party supplier who then ships it directly to the customer. Dropshipping eliminates the need for businesses to invest in inventory upfront, reducing carrying costs and inventory management complexities. However, it requires close coordination with suppliers and relies heavily on accurate order processing and shipping logistics.
6. Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI)
In VMI, suppliers have access to real-time sales data and inventory levels, allowing them to proactively manage the inventory and ensure timely replenishment. VMI reduces the burden on the customer in terms of inventory management, improves supply chain efficiency, and fosters strong supplier-customer relationships.
Benefits Of Inventory Management
Cost reduction: Efficient inventory management helps reduce costs associated with excess inventory and stockouts. By accurately forecasting demand and maintaining optimal stock levels, businesses can minimize carrying costs, such as warehousing, storage, insurance, and depreciation. Additionally, inventory management systems can identify slow-moving or obsolete items, enabling timely actions to prevent unnecessary inventory holding costs.
Improved cash flow: Effective inventory management allows businesses to optimize their cash flow. By minimizing excess inventory and streamlining procurement and production processes, companies can allocate their financial resources more efficiently and reduce the need for excessive working capital tied up in inventory. This can free up funds to invest in other areas of the business or improve liquidity.
Enhanced customer service: Maintaining proper inventory levels ensures that businesses can fulfill customer orders promptly and accurately. By having the right products in stock when customers need them, companies can improve customer satisfaction and loyalty. Inventory management systems enable businesses to track stock levels, monitor demand patterns, and implement just-in-time inventory strategies to meet customer demands effectively.
Increased operational efficiency: Efficient inventory management streamlines various operational processes, leading to increased overall efficiency. By utilizing inventory tracking systems and adopting automated inventory control techniques, businesses can eliminate manual errors, optimize order fulfillment processes, and reduce time and labor required for inventory management tasks. This allows employees to focus on value-added activities, improving productivity and operational efficiency.
Better decision-making: Inventory management systems provide businesses with real-time visibility into their inventory data, enabling informed decision-making. Accurate and up-to-date inventory information helps identify trends, analyze sales patterns, and make data-driven decisions regarding purchasing, production, and pricing strategies. This can lead to better inventory planning, optimized product assortment, and improved overall business performance.
Minimized stockouts and overstocks: Effective inventory management helps prevent stockouts (when products are out of stock) and overstocks (when excess inventory is held). By monitoring inventory levels, demand patterns, and lead times, businesses can avoid stockouts that can lead to lost sales and dissatisfied customers. Similarly, by optimizing reorder points and replenishment strategies, companies can minimize overstocks that tie up capital and increase carrying costs.
Reduced risk of obsolescence: Proper inventory management helps minimize the risk of holding obsolete or expired inventory. By tracking product lifecycles, implementing effective inventory rotation techniques (such as first-in, first-out - FIFO), and regularly reviewing stock levels, businesses can identify and take timely actions to prevent obsolescence. This reduces inventory write-offs and associated financial losses







0 Comments