Pharmacovigilance plays a significant role in ensuring the safety and efficacy of pharmaceutical products. In this article, we will explore the process and stages of pharmacovigilance.
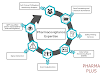
Stage 1: Data Collection
The first stage of the pharmacovigilance process involves the collection of data related to adverse drug reactions (ADRs) and other drug-related incidents. This information can come from various sources such as healthcare professionals, patients, clinical trials, scientific literature, regulatory authorities, and pharmaceutical companies.
Stage 2: Data Entry and Management
After data collection, the information is carefully entered into a pharmacovigilance database. Each reported case of an adverse event is documented, including details such as patient demographics, suspected drug, dosage, duration of use, the severity of the reaction, and any other relevant clinical information. The data is then managed and organized for further analysis.
Stage 3: Data Analysis and Signal Detection
In this stage, the collected data is analyzed to identify potential safety signals or patterns of adverse events associated with a particular drug. Statistical methods and data mining techniques are used to detect any unexpected or disproportionate reporting of adverse events. Signal detection aims to identify any potential safety concerns that may require further investigation.
Stage 4: Case Assessment and Causality
Once a safety signal is detected, further assessment is conducted to evaluate the relationship between the drug and the reported adverse event. This involves assessing the causality or the likelihood of the drug being responsible for the observed event. Various algorithms and scoring systems are used to determine the strength of the association between the drug and the adverse event.
Stage 5: Risk Management and Regulatory Reporting
If the causality assessment indicates a potential risk associated with the drug, risk management strategies are implemented. These strategies may include updating product labeling, issuing warnings, contraindications, or even withdrawal of the drug from the market if the risk outweighs the benefits. Regulatory authorities must be informed and provided with regular safety updates through periodic safety reports.
Stage 6: Communication and Dissemination of Safety Information
Pharmacovigilance aims to ensure that healthcare professionals, patients, and the general public are well-informed about the safety profile of drugs. Safety information and updates are communicated through various channels such as drug labels, package inserts, medication guides, public health advisories, educational materials, and online databases. This helps to enhance awareness and promote the safe and appropriate use of medications.
Stage 7: Monitoring and Evaluation
The final stage of the pharmacovigilance process involves continuous monitoring and evaluation of the safety profile of drugs. Ongoing surveillance is performed to detect any new safety signals, emerging risks, or long-term effects associated with the use of medications. This information is crucial for making informed decisions regarding the benefits and risks of drugs throughout their lifecycle.





0 Comments